Environment and Sustainable Development – Class 11 Economics, Simplified key notes, highlights, FAQs, and important questions with answers for Class 11 Economics Chapter 8: Environment and Sustainable Development. Perfect for students and SEO-optimized.

Environment and Sustainable Development – Class 11 Economics
Table of Contents
Introduction
The chapter “Environment and Sustainable Development” in Class 11 Economics discusses the relationship between economic development and environmental conservation. It emphasizes the need for sustainable development to ensure a balance between growth and environmental protection.

Key Notes
What is Environment?
- The environment includes all natural and human-made surroundings.
- Components of the environment:
- Natural: Air, water, soil, plants, and animals.
- Human-made: Buildings, infrastructure, and technology.
Functions of the Environment
- Supply of Resources: Provides natural resources like water, minerals, and forests.
- Assimilation of Waste: Absorbs waste generated by human activities.
- Sustains Life: Maintains ecological balance essential for life.
- Aesthetic Value: Offers beauty and recreational opportunities.
Environmental Problems
- Pollution: Air, water, soil, and noise pollution harm ecosystems.
- Deforestation: Leads to loss of biodiversity and climate change.
- Global Warming: Rising temperatures due to greenhouse gases.
- Overexploitation of Resources: Depletion of non-renewable resources.
Sustainable Development
- Defined as development that meets the needs of the present without compromising future generations’ ability to meet their needs.
- Key components:
- Economic growth.
- Social inclusion.
- Environmental protection.
Highlights of the Chapter
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Adopted by the United Nations in 2015.
- 17 goals addressing poverty, inequality, climate action, and more.
Strategies for Sustainable Development
- Use of Renewable Resources: Promote solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Efficient Resource Use: Minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
- Environmental Regulations: Enforce laws to control pollution and conserve biodiversity.
- Public Awareness: Educate people about environmental conservation.
Short Notes
- Carrying Capacity: The environment’s ability to sustain life without degradation.
- Global Commons: Shared resources like oceans and the atmosphere.
- Common Property Resources: Resources accessible to all, such as forests and rivers.
- Polluter Pays Principle: The polluter should bear the cost of managing pollution.
Important Questions and Answers
Q1. Define sustainable development.
Ans: Sustainable development refers to development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
Q2. List three strategies for sustainable development.
Ans:
- Use of renewable resources.
- Efficient resource utilization.
- Environmental regulation enforcement.
Q3. What are the functions of the environment?
Ans:
- Supply of resources.
- Assimilation of waste.
- Sustains life.
- Provides aesthetic value.
Previous Year Questions
Q1. Explain the concept of carrying capacity.
Ans: Carrying capacity refers to the maximum population size that the environment can sustain without being degraded over time. Exceeding this capacity leads to environmental problems.
Q2. Discuss the role of public awareness in sustainable development.
Ans: Public awareness plays a vital role in sustainable development by educating individuals and communities about the importance of conserving resources, adopting eco-friendly practices, and supporting policies that promote environmental sustainability.
Q3. What are the consequences of global warming?
Ans: Global warming leads to:
- Melting glaciers and rising sea levels.
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events.
- Loss of biodiversity.
- Disruption of ecosystems.
Q4. Define the polluter pays principle.
Ans: The polluter pays principle is an environmental policy concept where those responsible for pollution bear the costs of managing and mitigating its effects.
Why is sustainable development important?
Sustainable development ensures economic growth while protecting the environment and social equity for future generations.
What is the impact of deforestation?
Deforestation leads to loss of biodiversity, climate change, and disruption of ecological balance.
How to Learn This Chapter
- Understand Concepts: Focus on the definitions and functions of the environment.
- Relate to Real Life: Link concepts to current environmental issues.
- Practice Questions: Solve textbook and previous year’s questions.
- Use Diagrams: Visual aids like flowcharts help in better retention.
- Revise Regularly: Revise key points and strategies for sustainable development.
You can download textbook Q/A here.
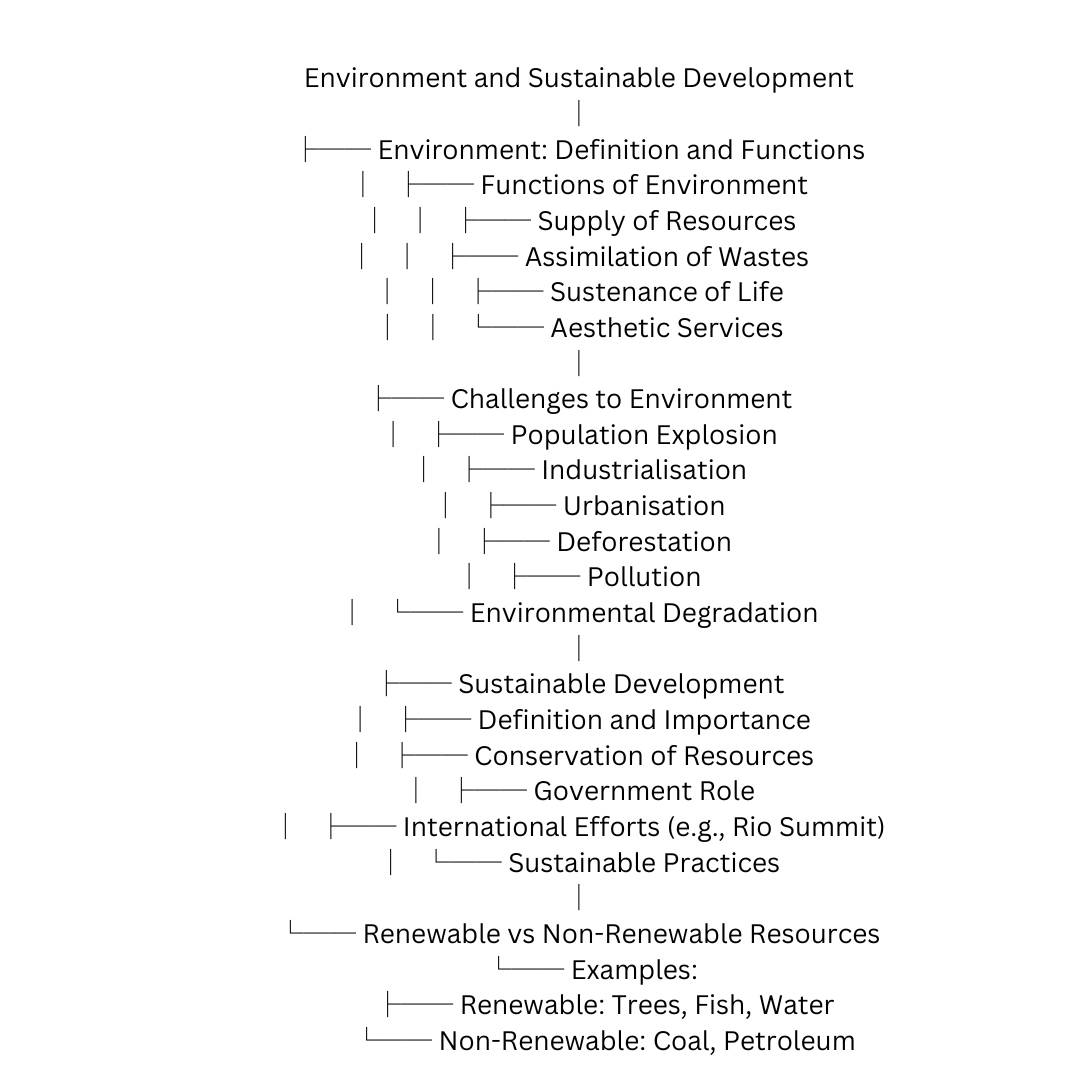
Flow Chart for Environment and Sustainable Development Class 11
Environment and Sustainable Development
│
├── Environment: Definition and Functions
│ ├── Functions of Environment
│ │ ├── Supply of Resources
│ │ ├── Assimilation of Wastes
│ │ ├── Sustenance of Life
│ │ └── Aesthetic Services
│
├── Challenges to Environment
│ ├── Population Explosion
│ ├── Industrialisation
│ ├── Urbanisation
│ ├── Deforestation
│ ├── Pollution
│ └── Environmental Degradation
│
├── Sustainable Development
│ ├── Definition and Importance
│ ├── Conservation of Resources
│ ├── Government Role
│ ├── International Efforts (e.g., Rio Summit)
│ └── Sustainable Practices
│
└── Renewable vs Non-Renewable Resources
└── Examples:
├── Renewable: Trees, Fish, Water
└── Non-Renewable: Coal, Petroleum
Chapter Summary Environment and Sustainable Development
The chapter “Environment and Sustainable Development” explores the intricate relationship between economic growth and environmental sustainability. The environment includes both natural and human-made elements and serves vital functions like resource supply, waste assimilation, and ecological balance. However, issues like pollution, deforestation, global warming, and overexploitation of resources threaten these functions.
Sustainable development is presented as the solution, emphasizing a balance between present needs and future generations’ requirements. Its three core components are economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection. The chapter highlights global efforts like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to combat pressing environmental challenges.
Strategies for achieving sustainable development include using renewable energy, optimizing resource efficiency, enforcing environmental regulations, and promoting public awareness. Concepts like carrying capacity, global commons, and the polluter pays principle underscore the need for collective responsibility in preserving the environment. By integrating economic and ecological goals, sustainable development ensures long-term well-being and resilience.
Understanding and applying these principles in real-life scenarios enable students to grasp the importance of conserving resources while fostering growth. This chapter serves as a foundation for addressing future environmental and developmental challenges effectively.
Thank you for reading Environment and Sustainable Development – Class 11 Economics.
for more articles like this you can our website : https://www.stationvidya.com/
You can follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/stationvidya/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/stationvidya/
You tube: https://www.youtube.com/@stationvidya/
We hope you’d loved the content , please do like, share and comment.
Subscribe for notification.
Environment and Sustainable Development Class 11

Leave a Reply