Science Class 8th Chapter 1 question answer. Get complete NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management. Ncert science class 8 chapter 1, class 8 ncert science pdf, chapter 1 solutions class 8 science ncert.

Science Class 8th Chapter 1 question answer
Chapter 1: Crop Production and Management – NCERT Solutions (2025-26)
🔹 Exercise Questions and Answers
Q1: Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
Question 1.
Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____
(b) The first step before growing crops is _______ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would ______ on top of the water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and ______ and ______ from the soil are essential.
Answer:
(a) crop
(b) preparation
(c) float
(d) water, nutrients
Full Sentence with Answers
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is preparation of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are essential.
Q2: Match items in Column A with those in Column B.
Question 2.
Match items in column A with those in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (i) Kharif crops | (e) Paddy and maize |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (b) Urea and super phosphate |
| (iv) Organic manure | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine, plant waste |
Q3: Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop:
- Paddy
- Maize
(b) Rabi crop:
- Wheat
- Gram
Q4: Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following:
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
(a) Preparation of Soil:
Preparation of soil is the first step in crop production. It involves loosening and turning the soil, which allows roots to penetrate deeply and helps air and water to reach them. This process is called tilling or ploughing. It improves soil aeration and enhances the activity of microbes. Levelling is then done to prepare the soil for sowing.
(b) Sowing:
Sowing is the process of placing seeds in the soil. Good quality, disease-free seeds are chosen. Farmers use tools like seed drills or traditional funnel-shaped tools to sow seeds at the correct depth and spacing to avoid overcrowding and ensure proper growth.
(c) Weeding:
Weeding is the removal of unwanted plants (weeds) that grow with crops. Weeds compete with crops for water, nutrients, sunlight, and space, affecting crop yield. Weeding is done manually using tools like khurpi or by spraying chemicals called weedicides.
(d) Threshing:
Threshing is the process of separating grain seeds from the chaff after harvesting. It is done manually or using machines like a combine, which performs both harvesting and threshing together.
Q5: Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
| Fertilisers | Manure |
|---|---|
| Man-made inorganic chemicals | Natural substances from decomposed plant/animal waste |
| Rich in specific nutrients (e.g., NPK) | Provides humus and improves soil texture |
| Prepared in factories | Made in fields or pits |
| Does not improve soil structure | Enhances water retention and microbial growth |
Q6: What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Irrigation is the artificial supply of water to crops at regular intervals. It helps in the growth and development of plants.
Two water-conserving irrigation methods:
- Sprinkler System: Pipes with rotating nozzles sprinkle water evenly across the field, simulating rain. Ideal for uneven land.
- Drip System: Delivers water drop-by-drop near plant roots. Very efficient and suitable for water-scarce areas.
Q7: If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season (rainy season), it will not grow properly. Wheat requires cool weather and less water, but kharif season has high temperatures and heavy rainfall, which can damage the crop or result in poor yield.
Q8: Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Continuous cropping depletes soil nutrients. Over time, the soil becomes less fertile and may not support healthy plant growth. To prevent this, farmers use manures, fertilizers, and adopt practices like crop rotation to restore soil nutrients.
Q9: What are weeds? How can we control them?
Weeds are unwanted plants that grow among crops and compete for nutrients, water, and sunlight.
Control methods:
- Manual removal: Using khurpi or hand weeding.
- Chemical control: Spraying weedicides like 2,4-D.
- Tilling: Uproots weeds before sowing.
Q10: Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
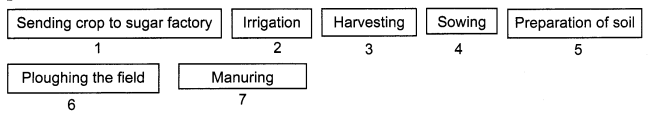
Correct order:
- Preparation of soil
- Ploughing the field
- Sowing
- Manuring
- Irrigation
- Harvesting
- Sending crop to sugar factory
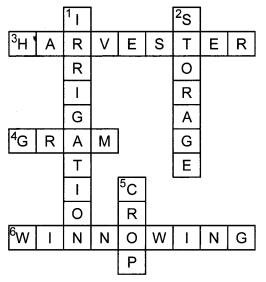
Q11: Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Across
3. Harvester
4. Gram
6. Threshing
Down
- Irrigation
- Storage
- Crop
Answer:
📘 Activity 1 (NCERT Textbook, Page 4)
Experiment:
Take a beaker and fill it halfway with water. Add a handful of wheat seeds and stir well. Wait for a few minutes.
🔍 Observation:
Most of the seeds sink to the bottom of the beaker, while a few seeds float on the surface.
✅ Explanation / Solution:
The seeds that sink are healthy and viable. The ones that float are damaged or hollow inside, making them lighter than water.
This activity helps in separating good seeds from damaged ones and is a common method used by farmers before sowing.
📘 Activity 2 (NCERT Textbook, Page 6)
Experiment:
- Germinate moong or gram seeds.
- Select 3 equal-sized seedlings.
- Prepare 3 glasses/vessels and mark them A, B, and C.
- Glass A: Soil + Cow dung manure
- Glass B: Soil + Urea (fertiliser)
- Glass C: Soil only (no addition)
Plant one seedling in each glass. Add equal water to all and keep in a safe place. Observe for 7–10 days.
🔍 Observation:
- Glass A (manure): Healthy, steady growth
- Glass B (urea): Rapid growth initially
- Glass C (plain soil): Least growth, weak seedling
✅ Explanation / Solution:
- Manure (Glass A) improves soil texture, retains water, and releases nutrients slowly.
- Fertiliser (Glass B) gives quick nutrients but may affect long-term soil quality.
- Plain soil (Glass C) lacks added nutrients, so the plant’s growth is slow and weak.
Conclusion:
Both manure and fertiliser support plant growth, but organic manure improves overall soil health and is safer for long-term use.
📘 Activity 3 – Solved
(Crop Production and Management | NCERT Science Class 8 | Page 12)
📝 Task:
Make the following table in your notebook and complete it with correct sources of food obtained from animals.
✅ Activity 3 – Table: Food from Animals
| S. No. | Food | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Milk | Cow, Buffalo, She-goat, She-camel |
| 2. | Meat | Goat, Hen, Pig, Duck, Sheep |
| 3. | Egg | Hen, Duck, Goose |
| 4. | Honey | Honey bee |
✅ Explanation:
This activity helps you understand that animals are an important source of food, just like plants.
- Milk comes from domesticated mammals.
- Meat and eggs are sources of protein and come from poultry and livestock.
- Honey is made by bees and collected from beehives.
📘 Crop Production and Management – One Word Questions & Answers
- Name the process of growing crops. → Agriculture
- What is the practice of growing two or more crops in the same field? → Cropping
- Name the tool traditionally used for tilling soil. → Plough
- Which crop is grown in the rainy season? → Paddy
- Which method is used for sowing seeds with a tractor? → Seed drill
- Name one Kharif crop. → Maize
- Name one Rabi crop. → Wheat
- What is the process of cutting and gathering crops? → Harvesting
- Name a natural method of irrigation. → Moat
- Which instrument is used to sprinkle fertilizers? → Sprayer
- What is the unwanted plant in the field called? → Weed
- What is used to remove weeds? → Hoe
- Name one modern method of irrigation. → Sprinkler
- Name one traditional method of irrigation. → Chain pump
- Which machine is used for harvesting? → Combine
- What is the process of separating grains from chaff? → Winnowing
- Which process involves loosening the soil? → Tilling
- What is added to soil to increase its fertility? → Manure
- Name one chemical fertilizer. → Urea
- What is the process of preserving grain in jute bags? → Storage
- Who provides food to the plant? → Root
- What is the use of manure? → Fertilization
- What type of soil is best for growing wheat? → Loamy
- What is the removal of weeds called? → Weeding
- Which tool is used to level the soil? → Leveller
- What is the uppermost fertile layer of soil called? → Topsoil
- Name the bacteria that fix nitrogen in legumes. → Rhizobium
- What is mixed with soil before sowing? → Manure
- Name a process used to improve soil structure. → Ploughing
- Which system of irrigation saves water? → Drip
- Tool used for loosening soil and removing weeds? → Hoe
- Traditional irrigation method using a pulley system? → Moat
- Which crop is first grown in nurseries before being transplanted? → Paddy
- Which organ of the plant absorbs water and nutrients? → Root
- Main nutrient replenished by growing legumes? → Nitrogen
- Which season do we grow mustard and wheat in? → Winter
- The solid waste from animals used as organic manure? → Dung
- Which element is most common in chemical fertilizers? → Nitrogen
- The process of allowing manure to decompose before use? → Composting
- Microorganisms that decompose organic matter? → Bacteria
- Device that helps cover seeds with soil after sowing? → Seed drill
- What is the function of Rhizobium bacteria? → Fixation
- What increases soil porosity and aeration naturally? → Earthworms
- Storage structure used by small farmers? → Bin
- Agricultural machine pulled by a tractor for tilling? → Cultivator
- What is the full form of NPK in fertilizers? → Nutrients
- The season when maize and cotton are grown? → Kharif
- Crop cutting festival celebrated in Punjab? → Baisakhi
- Undesirable plants competing with crops for resources? → Weeds
- Name of the lever-based traditional irrigation tool? → Rahat
You Can download pdf
That’s all for the Science Class 8th Chapter 1 question answer, ncert science class 8 chapter 1, class 8 ncert science pdf, chapter 1 solutions class 8 science ncert
Related Article: https://stationvidya.com/importance-of-waste-management-essay-in-500-words/
You can follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/stationvidya/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/stationvidya/
You tube: https://www.youtube.com/@stationvidya/
We hope you’d loved the content , please do like, share and comment.
Subscribe for notification

Leave a Reply